Services
- Home
- Diagnostic Procedures
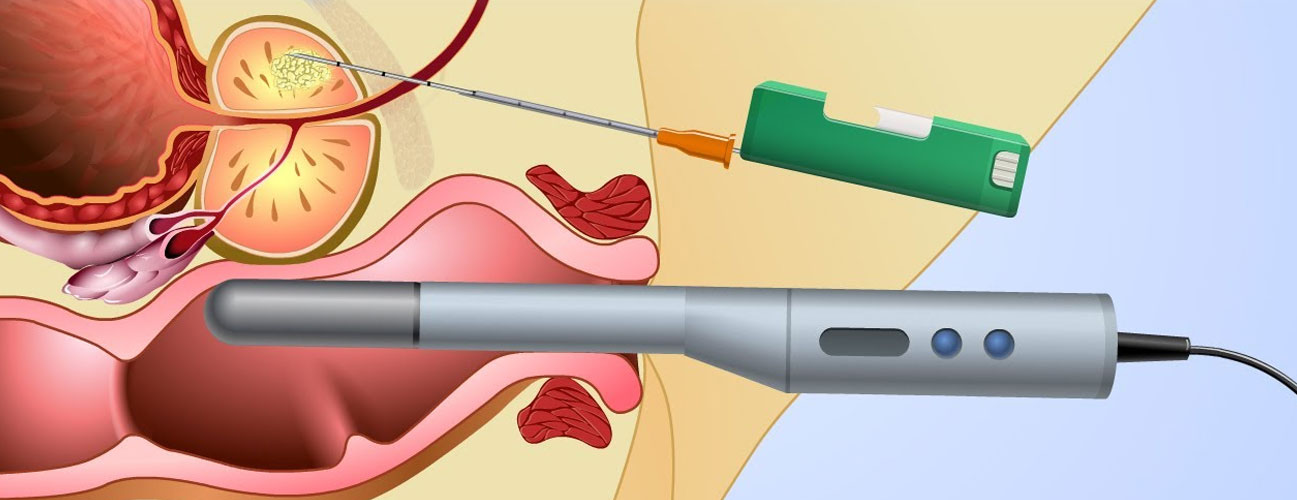
TRUS Biopsies
Transrectal ultrasound-guided (TRUS) biopsy is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate abnormalities in the prostate, often indicated by elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels or irregular findings in a digital rectal exam (DRE). During this procedure, an ultrasound probe is inserted into the rectum to create real-time images of the prostate. Guided by these images, a physician uses a biopsy needle to extract small tissue samples from specific areas within the prostate gland for analysis.
TRUS biopsies are typically performed in an outpatient setting under local anesthesia, ensuring minimal discomfort. The procedure itself usually takes 10–20 minutes. Patients may experience mild bleeding in urine, semen, or stool for a short period post-biopsy, which is generally self-limiting. Antibiotics are prescribed to reduce the risk of infection, which is a potential complication of the procedure.
TRUS biopsies play a crucial role in diagnosing prostate cancer and assessing prostate conditions, aiding in early detection and treatment decisions. While not without limitations, such as a slight risk of missing small tumors, this method is an effective and widely used diagnostic tool in urology. Follow-up care may involve further imaging or targeted biopsies if the results warrant additional investigation.
