Services
- Home
- Surgical Procedures
Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery (RIRS)
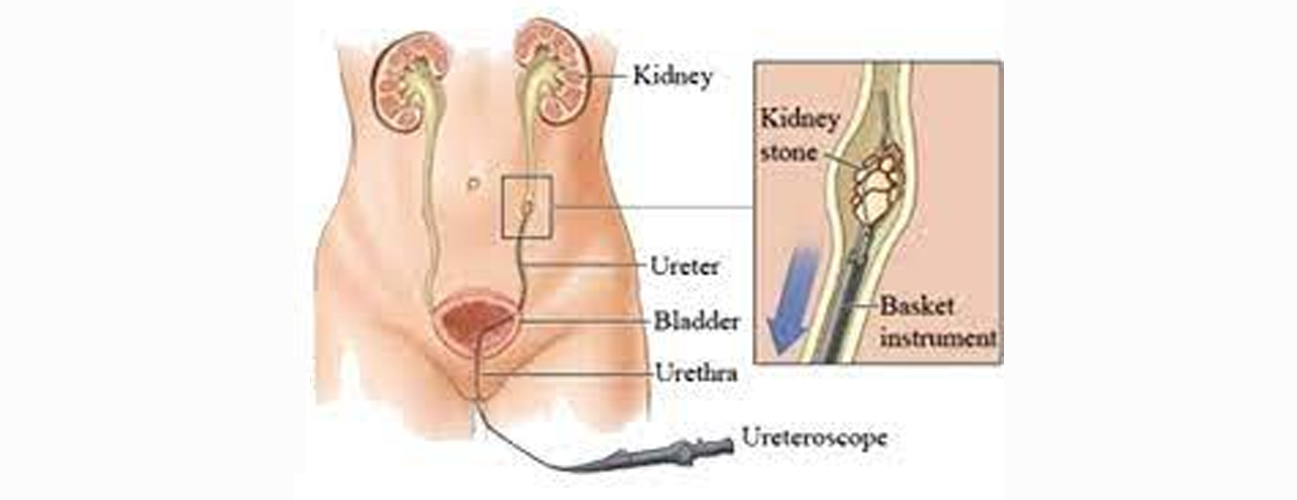
Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery (RIRS) is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat kidney stones, particularly those located within the renal pelvis or calyces. It involves the use of a flexible ureteroscope, which is inserted through the urethra, bladder, and ureter to reach the kidney. The scope is equipped with a camera, allowing the surgeon to visualize the stones and surrounding structures in real time.
During the procedure, small instruments are passed through the ureteroscope to fragment and remove the kidney stones. One of the most common techniques used is laser lithotripsy, where a laser fiber is used to break the stones into smaller, passable fragments. The procedure is typically performed under general or regional anesthesia, and in many cases, it eliminates the need for external incisions, reducing recovery times and minimizing complications.
RIRS is highly effective for treating stones that are difficult to access or too large to be passed naturally. It is often recommended for patients who have failed conservative treatments or have stones located in challenging anatomical areas. This procedure is associated with less postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and a quicker return to normal activities compared to traditional open surgery or percutaneous nephrolithotomy.
