Services
- Home
- Urinary Tract Infections
Epididymo Orchitis
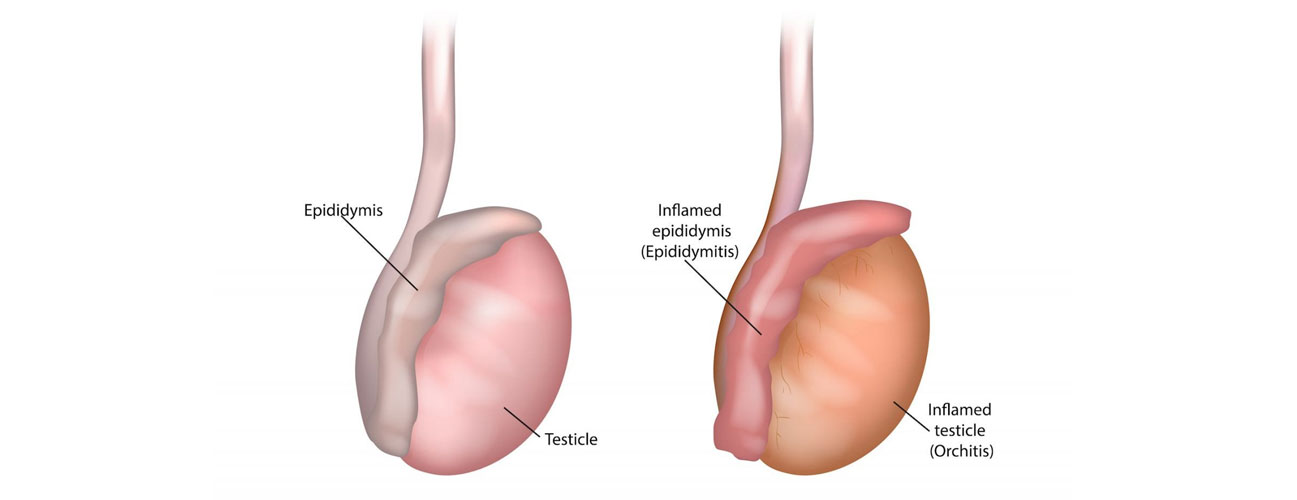
Epididymo-orchitis is an inflammation of the epididymis and testicle, typically caused by bacterial or viral infections. It commonly affects men aged 19 to 35 and can result from sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as chlamydia or gonorrhea, or from urinary tract infections (UTIs) in older men. The condition can also develop after a urinary catheterization or as a complication of prostate surgery.
Symptoms include unilateral testicular pain, swelling, tenderness, fever, and redness over the scrotum. The affected testicle may become enlarged and hard, and patients may experience discomfort or pain during urination or sexual intercourse. In some cases, there may be a discharge from the urethra, depending on the causative infection.
Diagnosis is based on clinical evaluation, patient history, and diagnostic tests like urine analysis, blood cultures, ultrasound, and possibly STI screenings. Ultrasonography can confirm the presence of epididymal or testicular swelling, increased blood flow, and the absence of abscesses.
Treatment typically includes antibiotics for bacterial infections, with broad-spectrum agents chosen initially until specific pathogens are identified. Pain relief, scrotal support, and rest are also recommended. In some cases, surgical drainage may be necessary if an abscess develops. Early intervention is essential to prevent complications like infertility or chronic pain.
