Services
- Home
- Urinary Tract Infections
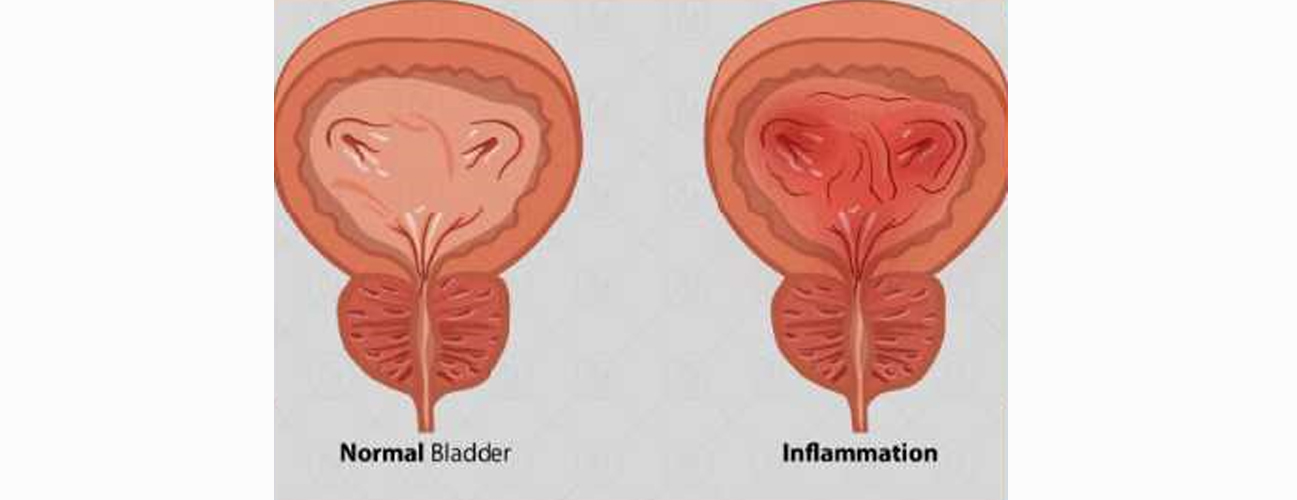
Bladder (Cystitis)
Cystitis is the medical term for inflammation of the bladder, most commonly caused by a bacterial infection. It is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI) and is more frequent in women due to the shorter length of the urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder. Common symptoms include a persistent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, lower abdominal pain, and sometimes blood in the urine (hematuria). Mild cases may resolve on their own, but recurrent or severe cystitis often requires antibiotics to prevent complications.
Cystitis can also have non-infectious causes, such as radiation therapy, certain medications, or irritants like feminine hygiene products or spermicides. Interstitial cystitis (IC), also known as painful bladder syndrome, is a chronic form of bladder inflammation without bacterial infection, causing long-term pelvic pain and urinary urgency.
Preventive measures include staying well-hydrated, practicing good hygiene, urinating regularly, and avoiding irritants. Cranberry supplements or probiotics may also help reduce UTI recurrence in some individuals. Persistent or severe cases should be evaluated by a healthcare provider to prevent kidney infection or chronic complications. With prompt treatment, most cases of cystitis resolve quickly and without lasting damage.
