Services
- Home
- Diagnostic Procedures
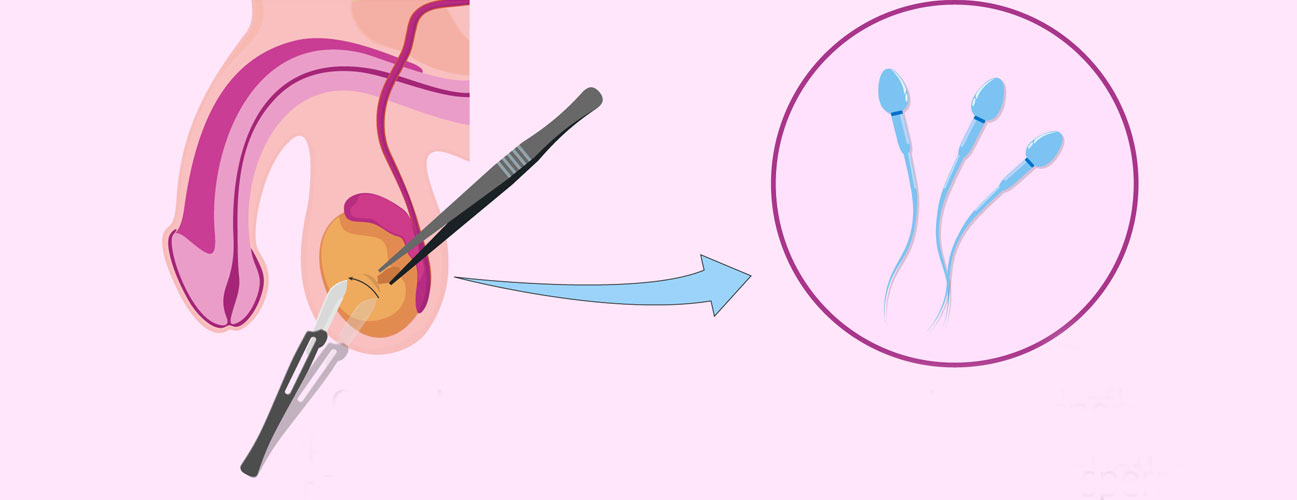
Testicular Biopsies
A testicular biopsy is a medical procedure where a small sample of tissue is taken from one or both testicles for examination. This procedure helps evaluate male infertility, diagnose testicular disorders, and detect abnormalities like testicular cancer. There are two primary types of testicular biopsies: open biopsy and percutaneous biopsy. In an open biopsy, a small incision is made in the scrotum to access the testicle, allowing for direct tissue sampling. A percutaneous biopsy, on the other hand, uses a thin needle inserted through the skin to obtain a tissue sample without a surgical incision.
Testicular biopsies are generally performed under local anesthesia, ensuring minimal discomfort. The procedure is often recommended for men with unexplained infertility, especially when sperm production issues are suspected. Additionally, testicular biopsies can aid in detecting infections, inflammation, or cancerous cells within the testicles, providing valuable insights for further treatment. After the biopsy, the sample is sent to a laboratory for microscopic examination, where specialists assess cellular structure, sperm production levels, and any signs of abnormal cell growth.
While testicular biopsies are relatively safe, some risks include infection, bleeding, or swelling. The results guide personalized treatment plans, such as fertility interventions or cancer treatment, helping optimize patient outcomes through targeted care.
